SONG Shengjie
List: 134. 加油站,135. 分发糖果,860.柠檬水找零,406.根据身高重建队列
134. 加油站gas-station,135. 分发糖果candy,860.柠檬水找零lemonade-change,406.根据身高重建队列queue-reconstruction-by-height
134. 加油站gas-station
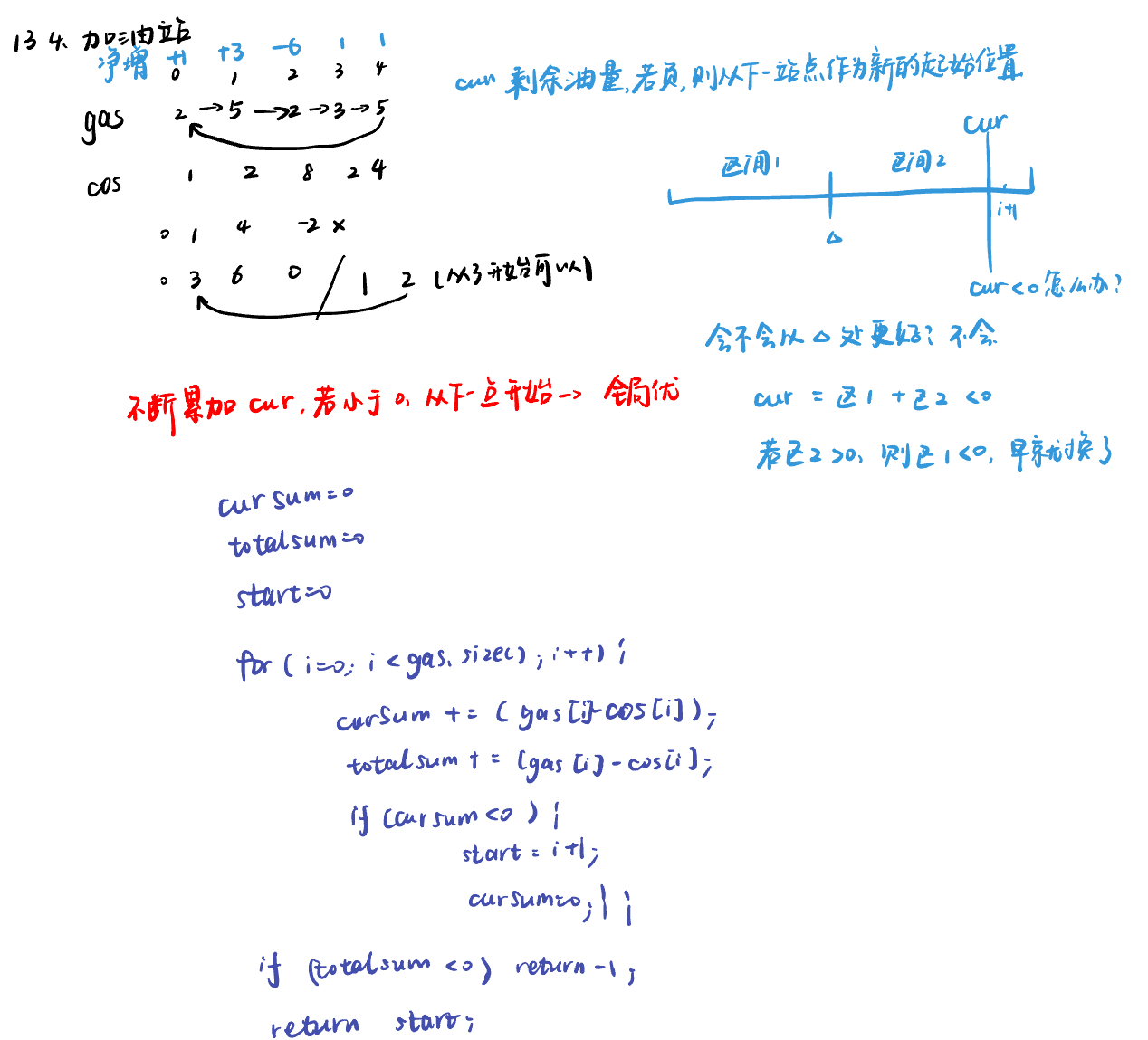
class Solution:
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
cur = 0
total = 0
start = 0
for i in range(len(gas)):
cur += gas[i] - cost[i]
total += gas[i] - cost[i]
if cur < 0:
cur = 0
start = i + 1
if total < 0:
return -1
return start
另一种方法:全局贪心选择
-
情况一:如果gas的总和小于cost总和,那么无论从哪里出发,一定是跑不了一圈的
-
情况二:rest[i] = gas[i]-cost[i]为一天剩下的油,i从0开始计算累加到最后一站,如果累加没有出现负数,说明从0出发,油就没有断过,那么0就是起点。
-
情况三:如果累加的最小值是负数,汽车就要从非0节点出发,从后向前,看哪个节点能把这个负数填平,能把这个负数填平的节点就是出发节点。
class Solution:
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
cur = 0 # 当前累计的剩余油量
minfuel = float('inf') # 从起点出发,油箱里的油量最小值
for i in range(len(gas)):
cur += gas[i] - cost[i]
if cur < minfuel:
minfuel = cur
if cur < 0:
return -1 # 情况1:整个行程的总消耗大于总供给,无法完成一圈
if minfuel > 0:
return 0 # 情况2:从起点出发到任何一个加油站时油箱的剩余油量都不会小于0,可以从起点出发完成一圈
for i in range(len(gas) - 1, -1, -1):
minfuel += gas[i] - cost[i]
if minfuel >= 0:
return i # 情况3:找到一个位置使得从该位置出发油箱的剩余油量不会小于0,返回该位置的索引
return -1
135. 分发糖果candy
本题涉及到一个思想,就是想处理好一边再处理另一边,不要两边想着一起兼顾,后面还会有题目用到这个思路

class Solution:
def candy(self, ratings: List[int]) -> int:
candy = [1] * len(ratings)
for i in range(1, len(ratings)):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]:
candy[i] = candy[i - 1] + 1
for i in range(len(ratings) - 2, -1, -1):
if ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]:
candy[i] = max(candy[i + 1] + 1, candy[i])
return sum(candy)
860.柠檬水找零lemonade-change

class Solution:
def lemonadeChange(self, bills: List[int]) -> bool:
five = 0
ten = 0
twenty = 0
for i in range(len(bills)):
if bills[i] == 5:
five += 1
if bills[i] == 10:
if five > 0:
five -= 1
ten += 1
else:
return False
if bills[i] == 20:
if five > 0 and ten > 0:
ten -= 1
five -= 1
twenty += 1
elif five >= 3:
five -= 3
twenty += 1
else:
return False
return True
406.根据身高重建队列queue-reconstruction-by-height

-
局部最优:优先按身高高的people的k来插入。插入操作过后的people满足队列属性
-
全局最优:最后都做完插入操作,整个队列满足题目队列属性
from typing import List
class Solution:
def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
# 第一步:对 people 列表进行排序
people.sort(key = lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]))
"""
这里使用了 Python 的列表排序方法 sort,并且指定了 key 参数。
key 参数是一个函数,用于指定排序的规则。
lambda x: (-x[0], x[1]) 是一个匿名函数,它接受一个元素 x(这里的 x 是 people 列表中的一个子列表 [h, k])。
-x[0] 表示按照身高 h 从高到低排序,因为前面加了负号,数值越大,排序越靠前。
x[1] 表示当身高相同时,按照 k 值从小到大排序。
例如,对于输入 [[7,0], [4,4], [7,1], [5,0], [6,1], [5,2]],排序后变为 [[7,0], [7,1], [6,1], [5,0], [5,2], [4,4]]。
"""
# 初始化一个空列表 que 用于存储最终的队列
que = []
# 第二步:遍历排序后的 people 列表,进行插入操作
for p in people:
# 根据每个人的 k 值将其插入到 que 列表的相应位置
que.insert(p[1], p)
"""
insert 方法用于在列表的指定位置插入元素。
p[1] 是每个人的 k 值,表示在最终队列中,身高大于或等于这个人的人在这个人前面的数量。
由于我们已经按照身高从高到低排序,所以在插入时,前面已经插入的人身高都大于或等于当前插入的人。
因此,直接将当前人插入到 que 列表的第 p[1] 个位置,就可以保证满足 k 值的要求。
例如,对于排序后的列表 [[7,0], [7,1], [6,1], [5,0], [5,2], [4,4]]:
- 首先插入 [7, 0],que 变为 [[7, 0]]。
- 接着插入 [7, 1],由于 k 值为 1,所以插入到索引为 1 的位置,que 变为 [[7, 0], [7, 1]]。
- 然后插入 [6, 1],由于 k 值为 1,所以插入到索引为 1 的位置,que 变为 [[7, 0], [6, 1], [7, 1]]。
- 以此类推,最终得到正确的队列。
"""
# 返回最终的队列
return que