SONG Shengjie
List: 图论理论基础,深度优先搜索理论基础,98. 所有可达路径,广度优先搜索理论基础
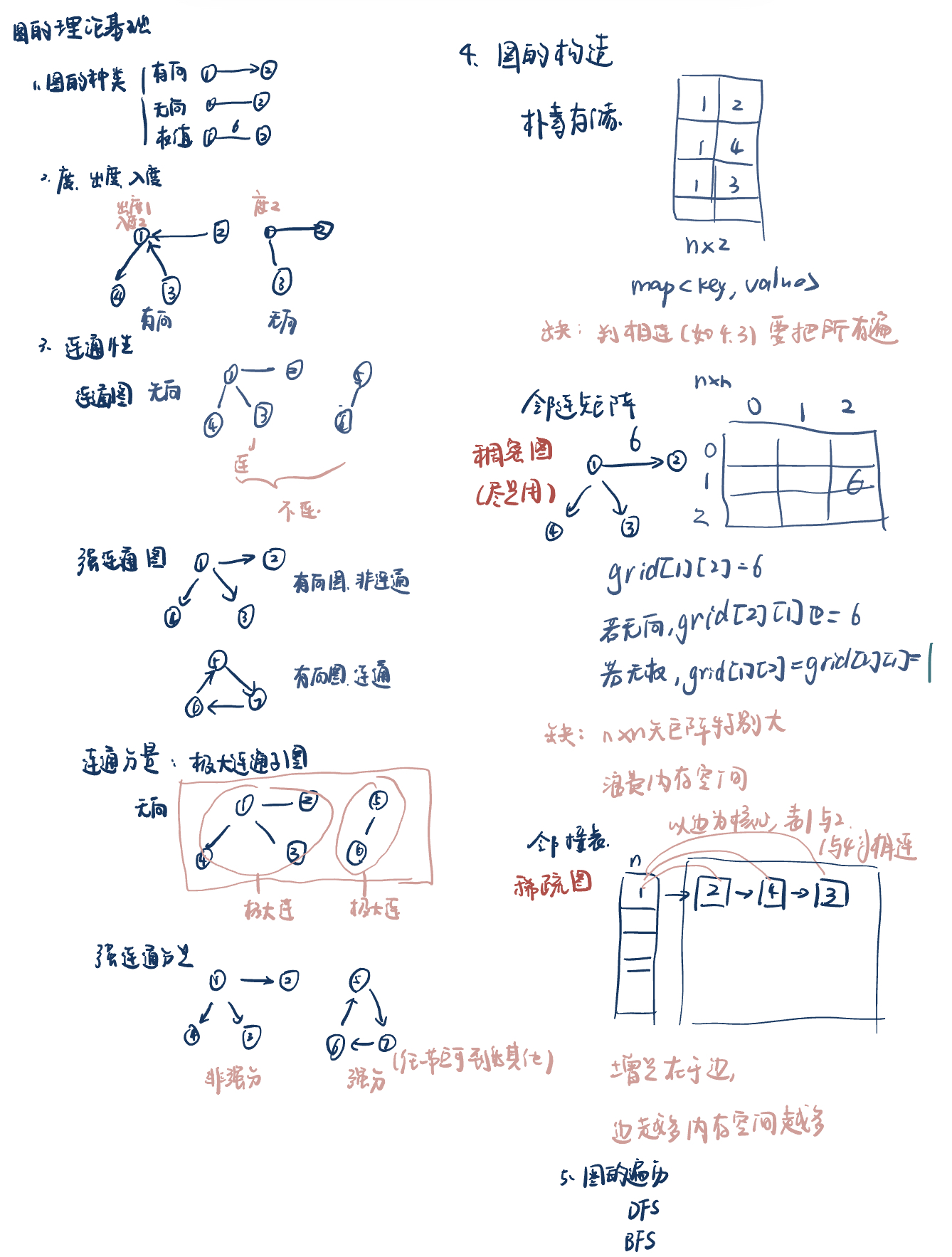
图论理论基础,,,,
图论理论基础
深度优先搜索理论基础
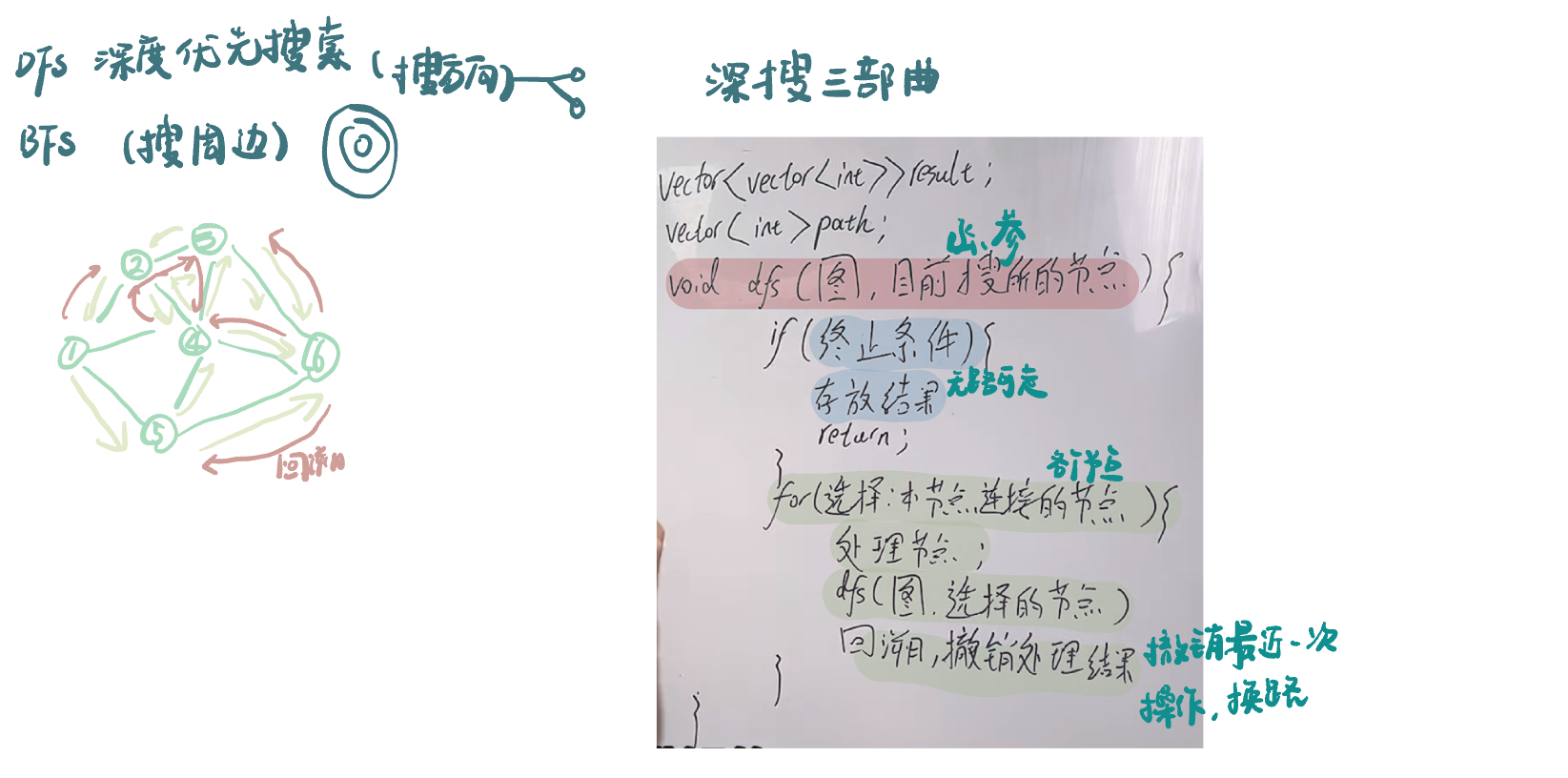
98. 所有可达路径

邻接矩阵法:
result = []
path = []
def dfs(graph, x, n):
if x == n:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if graph[x][i] == 1:
path.append(i)
dfs(graph, i, n)
path.pop()
def main():
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)]
for _ in range(m):
s, t = map(int, input().split())
graph[s][t] = 1
path.append(1)
dfs(graph, 1, n)
if not result:
print(-1)
else:
for p in result:
print(' '.join(map(str, p)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
邻接表法:
from collections import defaultdict
result = []
path = []
def dfs(graph, x, n):
if x == n:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in graph[x]: #和邻接矩阵的区别之处,及没有if语句
path.append(i)
dfs(graph, i, n)
path.pop()
def main():
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = defaultdict(list) #和邻接矩阵的区别之处
for _ in range(m):
s, t = map(int, input().split())
graph[s].append(t) #和邻接矩阵的区别之处
path.append(1)
dfs(graph, 1, n)
if not result:
print(-1)
else:
for p in result:
print(' '.join(map(str, p)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
广度优先搜索理论基础
