SONG Shengjie
List: 530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差,501.二叉搜索树中的众数,236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst,501.二叉搜索树中的众数find-mode-in-binary-search-tree,236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst
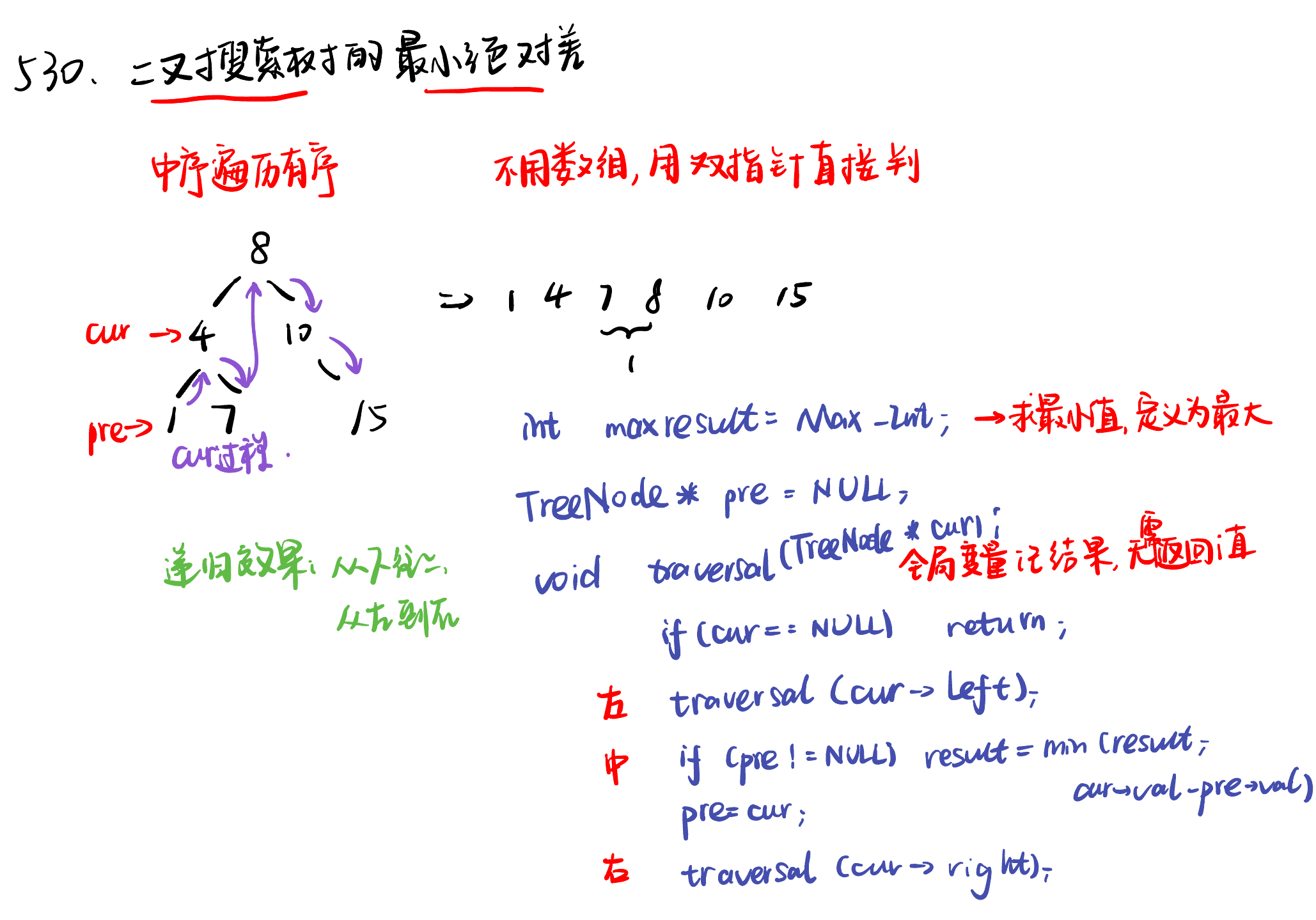
递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.result = float('inf')
self.pre = None #如果写成 self.pre = TreeNode(),那么在开始遍历时,self.pre 就被初始化为一个新的节点对象
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return
self.getMinimumDifference(root.left)
if self.pre:
self.result = min(self.result, root.val - self.pre.val)
self.pre = root
self.getMinimumDifference(root.right)
return self.result
迭代法:使用中序遍历
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
st = []
cur = root
pre = None
result = float('inf')
while cur or st:
if cur:
st.append(cur)
cur = cur.left
else:
cur = st.pop()
if pre:
result = min(result, cur.val - pre.val)
pre = cur
cur = cur.right
return result
501.二叉搜索树中的众数find-mode-in-binary-search-tree

递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.pre = None
self.count = 0
self.maxcount = 0
self.result = []
def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return
self.findMode(root.left)
# count的更新
if not self.pre:
self.count = 1
elif self.pre.val == root.val:
self.count += 1
else:
self.count = 1
# pre的更新
self.pre = root
# result的更新1
if self.count == self.maxcount:
self.result.append(root.val)
# maxcount的更新和result的实时更新2
if self.count > self.maxcount:
self.maxcount = self.count
self.result = []
self.result.append(root.val)
self.findMode(root.right)
return self.result
为什么没有这个技巧一定要遍历两次呢? 因为要求的是集合,会有多个众数,如果规定只有一个众数,那么就遍历一次稳稳的了。
迭代法:直接改中序遍历的逻辑即可,几乎不怎么需要变代码,直接改一下逻辑就好了
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.pre = None
self.count = 0
self.maxcount = 0
self.result = []
def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
st = []
cur = root
while st or cur:
if cur:
st.append(cur)
cur = cur.left
else:
cur = st.pop()
# count的更新
if not self.pre:
self.count = 1
elif self.pre.val == cur.val:
self.count += 1
else:
self.count = 1
# pre的更新
self.pre = cur
# result的更新1
if self.count == self.maxcount:
self.result.append(cur.val)
# maxcount的更新和result的实时更新2
if self.count > self.maxcount:
self.maxcount = self.count
self.result = []
self.result.append(cur.val)
cur = cur.right
return self.result
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree
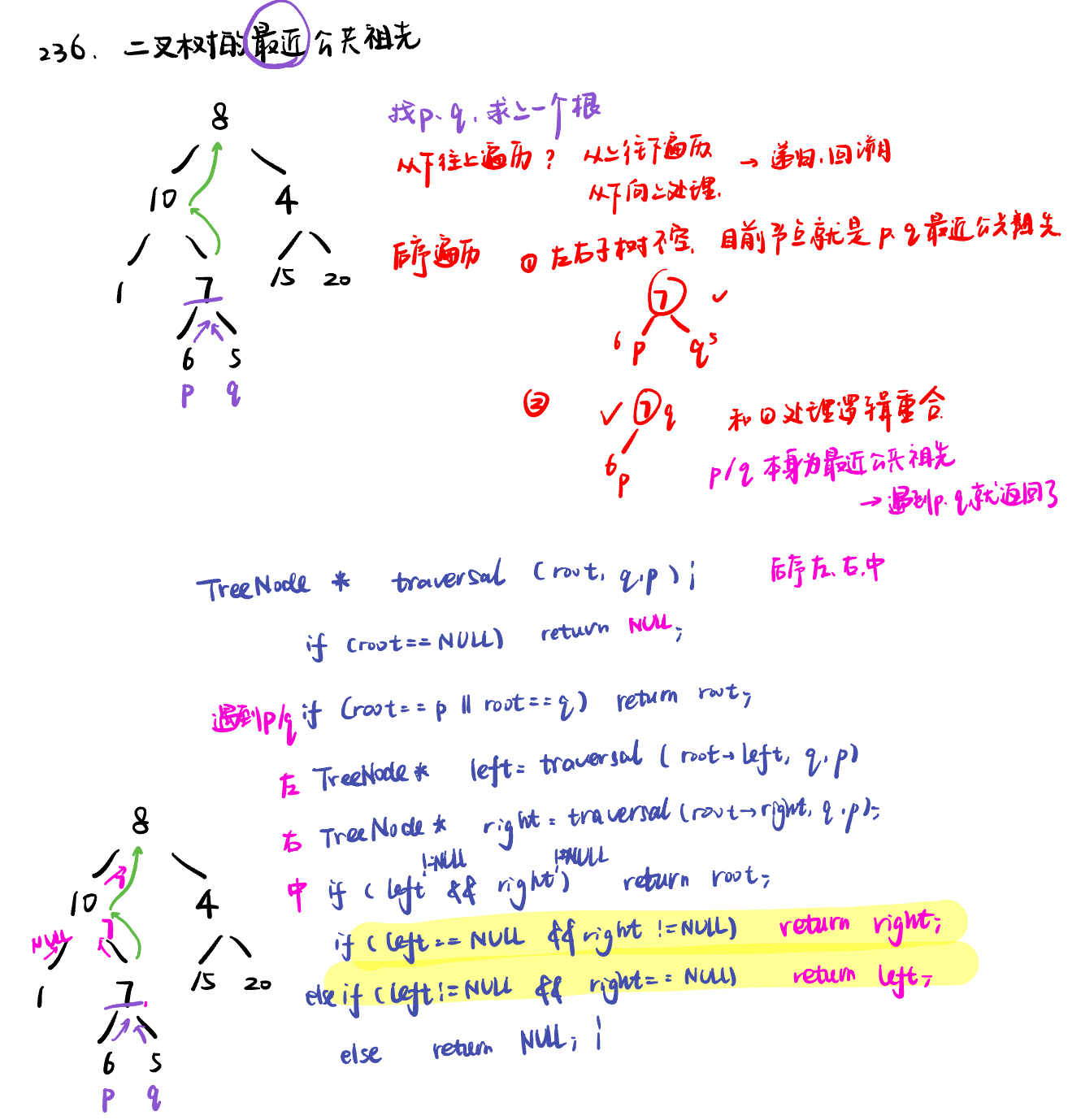
在递归函数有返回值的情况下:如果要搜索一条边,递归函数返回值不为空的时候,立刻返回,如果搜索整个树,直接用一个变量left、right接住返回值,这个left、right后序还有逻辑处理的需要,也就是后序遍历中处理中间节点的逻辑(也是回溯)。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if not root:
return
if root == p or root == q:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if left and right:
return root
elif not left and right:
return right
elif left and not right:
return left
else:
return
- 总结:
求最小公共祖先,需要从底向上遍历,那么二叉树,只能通过后序遍历(即:回溯)实现从底向上的遍历方式。
在回溯的过程中,必然要遍历整棵二叉树,即使已经找到结果了,依然要把其他节点遍历完,因为要使用递归函数的返回值(也就是代码中的left和right)做逻辑判断。
要理解如果返回值left为空,right不为空为什么要返回right,为什么可以用返回right传给上一层结果。