SONG Shengjie
List: 找树左下角的值,路径总和(力扣112/113),从中序分别与后序、前序遍历序列构造二叉树(含力扣105/106)
513.找树左下角的值find-bottom-left-tree-value,112. 路径总和path-sum,106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal
513.找树左下角的值find-bottom-left-tree-value

递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findBottomLeftValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.maxdepth = float('-inf')
self.result = None
def getdepth(node, depth):
if not node.left and not node.right:
if depth > self.maxdepth:
self.maxdepth = depth
self.result = node.val #只有判断是叶子,才运行
return
if node.left:
getdepth(node.left, depth + 1)
if node.right:
getdepth(node.right, depth + 1)
getdepth(root, 0)
return self.result
迭代法:
只需要在层次遍历过程中,记录每一行的第一个节点的值并不断迭代这个值,最后一次循环得到的就是最后一行最左的元素。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findBottomLeftValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return
que = deque([root])
result = 0
while que:
size = len(que)
for i in range(size):
node = que.popleft()
if i == 0:
result = node.val
if node.left:
que.append(node.left)
if node.right:
que.append(node.right)
return result
112. 路径总和path-sum
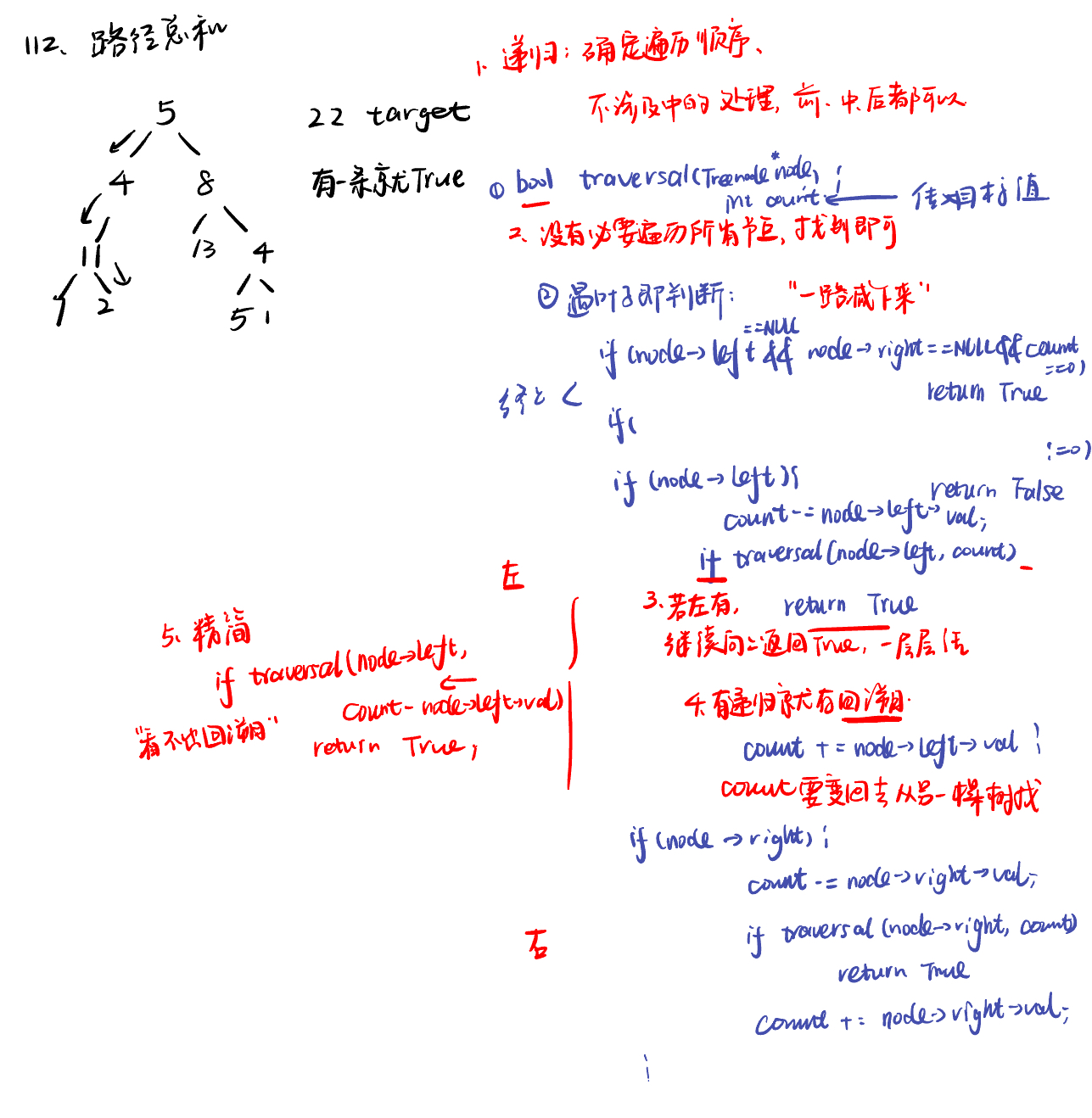
递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
return self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val) #由于没有对中处理,需要先把根节点去掉
def traversal(self, node, count) :
if not node.left and not node.right and count == 0:
return True
if not node.left and not node.right and count != 0:
return False
if node.left:
count -= node.left.val
if self.traversal(node.left, count):
return True
count += node.left.val
if node.right:
count -= node.right.val
if self.traversal(node.right, count):
return True
count += node.right.val
return False
- 精简版:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
if not root.left and not root.right and targetSum == root.val:
return True
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
迭代法
此时栈里一个元素不仅要记录该节点指针,还要记录从头结点到该节点的路径数值总和。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
# 此时栈里要放的是pair<节点指针,路径数值>
st = [(root, root.val)]
while st:
node, path_sum = st.pop()
# 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
if not node.left and not node.right and path_sum == targetSum:
return True
# 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
if node.right:
st.append((node.right, path_sum + node.right.val))
# 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
if node.left:
st.append((node.left, path_sum + node.left.val))
return False
相关题目:
[113.路径之和Ⅱ](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/description/)
区别在于要找到所有路径。所以递归函数不要返回值.
递归法
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
self.result = []
self.path = []
if not root:
return self.result
self.path.append(root.val)
self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
return self.result
def traversal(self, node, count):
if not node.left and not node.right and count == 0:
self.result.append(self.path[:])
return
if not node.left and not node.right:
return
if node.left:
self.path.append(node.left.val)
count -= node.left.val
self.traversal(node.left, count)
count += node.left.val
self.path.pop()
if node.right:
self.path.append(node.right.val)
count -= node.right.val
self.traversal(node.right, count)
count += node.right.val
self.path.pop()
return
迭代法
需要记录下来path的路径,就是多了一个值去记录累加。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
st = [(root, [root.val])]
res = []
while st:
node, path = st.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right and sum(path) == targetSum:
res.append(path)
if node.right:
st.append((node.right, path + [node.right.val]))
if node.left:
st.append((node.left, path + [node.left.val]))
return res
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal

# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
#后序数组为空
if len(postorder) == 0:
return None
#后序数组最后一个元素是根节点
rootvalue = postorder[-1]
root = TreeNode(rootvalue)
if len(postorder) == 1: #优化
return root
#寻找中序数组位置作为切割点
for i in range(len(inorder)):
if inorder[i] == rootvalue:
index = i
break
#切中序数组
leftin = inorder[:index]
rightin = inorder[index + 1:]
#切后序数组
leftpost = postorder[:len(leftin)]
rightpost = postorder[len(leftin): - 1]
#递归处理左右区间
root.left = self.buildTree(leftin, leftpost)
root.right = self.buildTree(rightin, rightpost)
return root
相关题目:
思路完全一致,注意切割区间的范围,左闭右开。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
#前序数组为空
if len(preorder) == 0:
return None
#前序数组第一个元素是根节点
rootvalue = preorder[0]
root = TreeNode(rootvalue)
if len(preorder) == 1: #优化
return root
#寻找中序数组位置作为切割点
for i in range(len(inorder)):
if inorder[i] == rootvalue:
index = i
break
#切中序数组
leftin = inorder[:index]
rightin = inorder[index + 1:]
#切前序数组
leftpre = preorder[1:len(leftin) + 1]
rightpre = preorder[len(leftin) + 1:]
#递归处理左右区间
root.left = self.buildTree(leftpre, leftin)
root.right = self.buildTree(rightpre, rightin)
return root