SONG Shengjie
二叉树综合:递归的应用、二叉搜索树
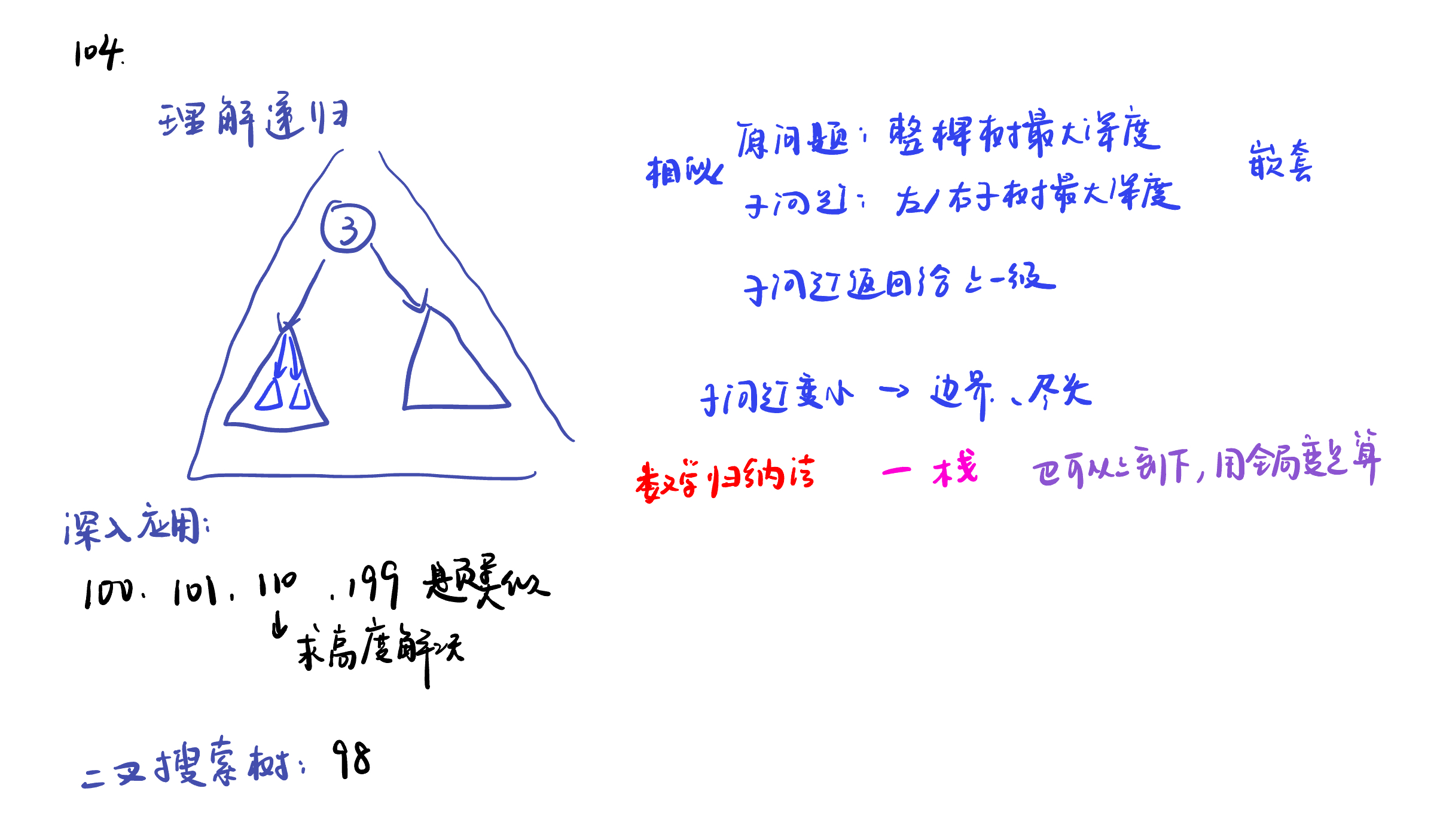
199题的递归法:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
#递归法
ans = []
def f(node, depth):
if not node:
return
if depth == len(ans):
ans.append(node.val)
f(node.right, depth + 1)
f(node.left, depth + 1)
f(root, 0)
return ans
98.二叉搜索树
前序遍历:先判断,再递归
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
x = root.val
return left < x < right and self.isValidBST(root.left, left, x) and self.isValidBST(root.right, x, right)
中序遍历:比较上一个节点
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
pre = -inf
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
if not self.isValidBST(root.left):
return False
if root.val <= self.pre:
return False
self.pre = root.val
return self.isValidBST(root.right)
后序遍历:先递归,再判断
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
# 左边、右边的最大值、最小值都要比较,空节点返回一个正无穷、负无穷
def f(node):
if not node:
return inf, -inf
lmin, lmax = f(node.left)
rmin, rmax = f(node.right)
x = node.val
if x <= lmax or x >= rmin:
return -inf, inf
return min(lmin, x), max(rmax, x)
return f(root)[1] != inf